Embarking on the journey to a secure and fulfilling retirement requires a comprehensive understanding of the intricate world of workplace retirement plans. This exploration encompasses not only traditional pensions but also the widely utilized 401(k)s, shedding light on the multifaceted aspects that play a pivotal role in shaping your financial future. Additionally, we will unravel the benefits of Roth IRAs, presenting a holistic view of the diverse financial tools available to individuals in the workforce.
Navigating the complexities of these retirement instruments demands more than a cursory glance; it calls for a deep dive into their structures, advantages, and potential pitfalls. As we delve into this discussion, the aim is to empower you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions, ultimately maximizing your savings potential and steering you toward a retirement that aligns seamlessly with your aspirations.
Decoding Workplace Retirement Plans
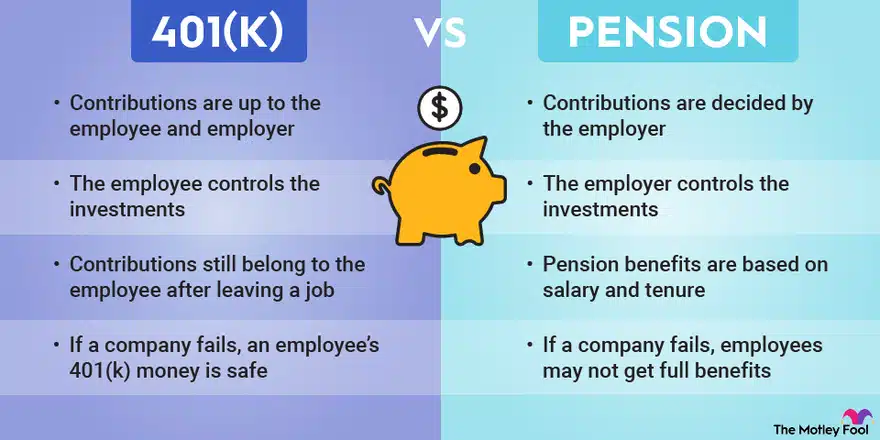
Workplace retirement plans offer a valuable avenue for saving for your golden years. These plans, often sponsored by employers, provide tax advantages and the option for employer contributions, making them an attractive option for long-term savings. Two common types of workplace retirement plans include pensions and 401(k)s.
Pensions
Pensions are traditional workplace retirement plans that provide a guaranteed stream of income upon retirement. Employer contributions and investment earnings typically determine the level of pension benefits.
401(k)s
401(k) workplace retirement plans allow employees to make pre-tax contributions from their paychecks. Employers may also match employee contributions, further boosting retirement savings.
The Pros and Cons of Pension Plans
Pension plans offer several advantages, including guaranteed income, portability, and protection from market fluctuations. However, they may also have drawbacks, such as vesting periods and potential employer financial risk.
Advantages of Pension Plans:
- Guaranteed income: Pensions provide a steady stream of income in retirement, offering financial security and peace of mind.
- Portability: Pension benefits are generally portable, meaning they can be transferred to another employer if you change jobs.
- Protection from market fluctuations: Pension benefits are not directly tied to market performance, providing stability and protection from market downturns.
Disadvantages of Pension Plans:
- Vesting periods: Pension benefits may not be fully vested until you have worked for a certain number of years, meaning you may not be entitled to the full benefit if you leave the employer before vesting.
- Employer financial risk: The financial health of the employer can impact the funding and stability of pension plans.
Navigating the World of 401(k)s
In the realm of employer-sponsored workplace retirement plans, 401(k)s have emerged as a foundational pillar, providing individuals with a strategic means of saving for their golden years. These plans offer a dynamic interplay of flexibility, tax advantages, and the potential for employer contributions, making them a popular choice for those seeking to build a secure financial future. As you embark on your journey to understand 401(k)s, it’s crucial to grasp key components that shape these plans and influence your retirement strategy.
Understanding 401(k)s:
- Contribution limits: One notable feature of 401(k)s is the existence of annual contribution limits. These limits, contingent on factors such as age and other considerations, serve as guidelines for individuals looking to optimize their retirement savings while adhering to regulatory boundaries.
- Employer matches: A compelling aspect of 401(k) plans is the prospect of employer matches. Many companies incentivize their employees’ workplace retirement plans by contributing a portion that mirrors the employee’s own contribution. This employer match serves as a valuable boost to the overall savings, enhancing the potential for a more robust retirement fund.
- Investment options: Beyond the financial contributions, 401(k)s present a diverse array of investment options. This flexibility empowers individuals to tailor their portfolios to align with their unique risk tolerance and long-term retirement objectives. From conservative investment choices to more aggressive strategies, the range of options allows for a personalized approach to wealth accumulation.
Pros and Cons of 401(k)s
Navigating the landscape of 401(k) plans involves considering both the advantages and potential drawbacks, allowing individuals to make well-informed choices for their financial future.
Advantages of 401(k)s:
- Tax Advantages: Contributions to a 401(k) are typically tax-deductible, providing immediate benefits by lowering taxable income.
- Employer Contributions: The potential for employer matches can significantly accelerate the growth of your retirement savings.
Disadvantages of 401(k)s:
- Early Withdrawal Penalties: Accessing funds before the specified retirement age can result in penalties, limiting the flexibility of using the money in unforeseen circumstances.
- Limited Investment Control: While there are various investment options, the choices within a 401(k) may be more restricted compared to individual investment accounts.

Maximizing Employer Contributions
In the realm of workplace retirement plans, optimizing employer contributions is a pivotal strategy to enhance your retirement savings through plans like the 401(k). A fundamental step in this process involves a thorough understanding of your employer’s matching policy, including the maximum contribution they are willing to match. To capitalize on this financial incentive, it is advisable to contribute at least up to the level specified by your employer. However, for those in a favorable financial position, going beyond the matched contributions can further amplify the growth of your retirement fund.
Tips to Maximize Employer Contributions:
- Frequent Contribution Assessments: Regularly review your financial situation and reassess your contribution strategy. If your circumstances improve, consider adjusting your contributions to take full advantage of the employer match.
- Automate Contributions: Set up automatic contributions from your paycheck to ensure consistency and discipline in your savings approach. Automation simplifies the process, making it easier to stay on track with your retirement goals.
- Utilize Salary Increases: When you receive a salary increase, consider allocating a portion of it towards your retirement contributions. This is an opportune time to boost your savings without impacting your current budget significantly.
By comprehensively grasping your employer’s policies and strategically adjusting your contributions, along with incorporating these additional tips, you can unlock the full potential of employer-sponsored workplace retirement plans, charting a course towards a more financially secure retirement.
The Roth IRA Advantage
In the absence of workplace retirement plans, individuals can turn to Roth IRAs as a compelling alternative to bolster their retirement savings. Offering a unique set of advantages, Roth IRAs seamlessly integrate into retirement planning, providing an avenue for tax-efficient wealth accumulation. While not workplace retirement plans, these individual retirement accounts empower individuals to take proactive steps toward securing their financial future.
Benefits of Roth IRAs:
- Tax-free withdrawals: Qualified Roth IRA withdrawals in retirement are tax-free, providing a stream of income without additional tax burdens.
- Contribution flexibility: Roth IRAs allow for tax-free withdrawals of contributions at any time, without penalty.
- Eligibility: Roth IRAs have income eligibility limits, but they are generally accessible to a wide range of individuals.
Weighing the Pros and Cons of Roth IRAs
Roth IRAs offer several advantages, but they also have some potential drawbacks. Understanding the pros and cons can help you decide if a Roth IRA is right for you.
Advantages of Roth IRAs:
- Tax-free withdrawals: Tax-free withdrawals in retirement are a significant benefit, particularly in higher tax brackets.
- Contribution flexibility: The ability to withdraw contributions tax-free provides added flexibility in financial planning.
- Tax-free growth: Investment earnings in Roth IRAs grow tax-free, further boosting savings potential.
Disadvantages of Roth IRAs:
- Income limits: Roth IRAs have income eligibility limits, which may restrict participation for higher-income earners.
- Tax implications for early withdrawals: Early withdrawals of investment earnings may be subject to taxes and penalties.
- Limited contribution flexibility: Contributions to Roth IRAs are made with after-tax dollars, which may limit the amount you can save annually.
The Role of Roth IRAs in Retirement Planning
Roth IRAs can complement workplace retirement plans and provide additional flexibility and tax benefits. Here are some scenarios where diversifying retirement savings with a Roth IRA may be beneficial:
- If you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement, Roth IRAs can provide tax-free income in the future.
- If you prioritize flexibility and the ability to withdraw contributions without penalty, Roth IRAs offer this advantage.
- If you are younger and have a longer time horizon for investment growth, Roth IRAs can benefit from tax-free compounding.
Making Informed Choices
In the realm of retirement savings, careful consideration and informed decision-making are paramount for optimizing your strategy toward a secure and fulfilling future. Key factors to weigh when contemplating workplace retirement plans and Roth IRAs encompass:
Initiate your financial planning journey by assessing long-term retirement goals and envisioning the desired lifestyle. This involves a thorough consideration of your preferred retirement age and the various factors influencing this pivotal decision. Additionally, evaluating your present financial situation, encompassing income, expenses, and existing debts, provides a comprehensive foundation for sound decision-making.
Delving into income considerations is essential for crafting a realistic retirement savings plan. Understanding your current income and projecting future changes sets the stage for informed choices. Further, recognizing the income eligibility limits for Roth IRAs and contemplating their impact on your savings options is crucial. Equally important is considering the tax implications associated with contributions to both workplace retirement plans and Roth IRAs, aligning your decisions with your overarching financial objectives.
Tax considerations play a vital role in shaping your retirement strategy. Evaluate your current tax bracket and anticipate shifts in retirement, allowing you to make nuanced decisions regarding pre-tax and after-tax contributions. A comprehensive understanding of the tax implications tied to withdrawals from workplace retirement plans and Roth IRAs adds an essential layer to your financial planning, ensuring a well-rounded approach to your retirement journey.

Workplace retirement plans and Roth IRAs are powerful tools for securing your financial future. By understanding the nuances of each option and making informed decisions based on your individual circumstances, you can effectively plan for a comfortable and fulfilling retirement. Remember, it’s always advisable to consult with a financial advisor to get personalized guidance and recommendations tailored to your specific financial situation.







Informative…